What is Software?
At its core, the definition of software refers to a set of instructions that enable a computer or electronic device to perform specific tasks or functions. These instructions are written in a programming language and are executed by the computer's central processing unit (CPU). Software is intangible and contrasts with the physical components of a computer, such as hardware.
Examples of Software:
Software comes in various forms and serves a multitude of purposes. For example, there are operating systems like Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Linux. Then there’s productivity software, such as Microsoft Office or Google Workspace, that assist users in creating documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
There’s also entertainment software, like video games and multimedia applications, that offer users recreational experiences. Things like web browsers, antivirus programs, and mobile apps are also examples of software.
What are the Main Types of Software?
System vs Application Software
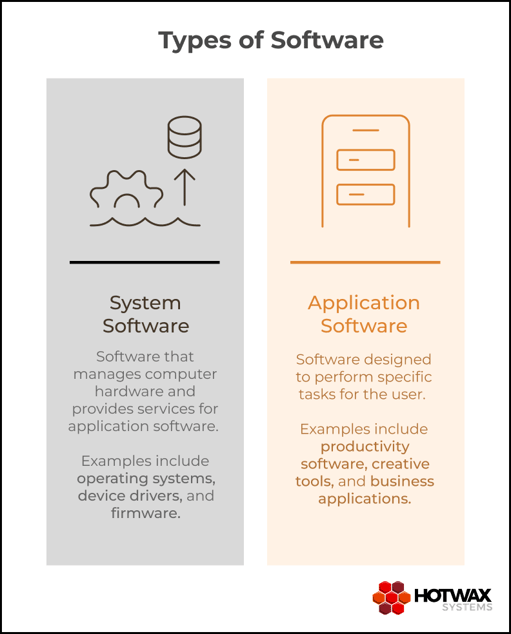
Software can generally be divided into two major categories: system software and application software.
System Software
System software forms the foundation of every computing environment. It operates quietly behind the scenes, coordinating how hardware and application software communicate with one another.
This category includes operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, which manage memory, processors, and device interfaces to ensure your applications run efficiently. It also covers utility programs like disk management tools, antivirus software, and system monitors that maintain performance and security.
In addition, device drivers serve as translators between the operating system and hardware components, while firmware provides low-level control embedded directly into devices like routers or printers.
Together, these programs handle the invisible but essential work of stability, performance, and resource allocation making sure everything else, from your web browser to enterprise applications, runs reliably and efficiently.
Application Software
Application software is any software built for end-users — from spreadsheets and video editors to ERP systems.
Within this broad category, Business & Enterprise Software is the segment that powers organizational functions like finance, HR, logistics, manufacturing, and customer management.
1. Productivity & Collaboration Software
Tools that help people work, communicate, and stay organized.
- Word processing, spreadsheets, presentations
- Messaging, video conferencing, shared workspaces
Examples: Microsoft Office, Google Workspace, Slack, Zoom, Notion
2. Creative, Media & Entertainment Software
Applications used for creating or consuming digital content.
- Graphic design, video editing, animation, UI/UX design
- Streaming, gaming, music production, AR/VR platforms
Examples: Adobe Creative Cloud, Figma, Blender, Netflix, Spotify, Steam
3. Education & Training Software
Platforms that enable digital learning, teaching, and skill development.
- Virtual classrooms, eLearning platforms, assessments, language learning
Examples: Coursera, Moodle, Blackboard, Duolingo
4. Utilities, Security & System Tools
Software that supports, protects, or optimizes devices and systems.
- Antivirus, encryption, system cleanup, backup, performance tools
Examples: Norton, Bitdefender, CCleaner, WinZip
5. Engineering, Scientific & Industry-Specific Tools
Specialized software built for research, simulation, design, and niche industries.
- CAD, simulation, data modeling, medical systems, lab analysis
- Sector-specific solutions (e.g., healthcare, aviation, logistics)
Examples: MATLAB, AutoCAD, ANSYS, Epic Systems, Meditech
6. Business & Enterprise Software
The operational core of modern organizations.
- These systems automate, monitor, and connect critical business processes across departments — finance, HR, manufacturing, logistics, and more.
Examples: SAP, Salesforce, Oracle, Apache OFBiz, HotWax Accelerator
|
Software Type |
What It Does |
|
Manages billing, budgeting, expenses, taxation, and financial reporting. |
|
|
Centralizes customer data to improve sales, service, and retention. |
|
|
Human Resource Management (HRM) |
Handles recruitment, payroll, attendance, and workforce analytics. |
|
Project Management Software |
Plans, tracks, and manages team projects and cross-functional workflows. |
|
Coordinates suppliers, logistics, procurement, and distribution of goods. |
|
|
Controls inventory storage, picking, packing, and fulfillment operations. |
|
|
Manages order capture, payment, inventory allocation, and delivery routing. |
|
|
Tracks production processes and machine performance in real time on the factory floor. |
|
|
Integrates finance, HR, supply chain, manufacturing, and operations into one system. |
|
|
Stores and manages detailed product data across channels from one source of truth. |
These platforms form the backbone of enterprise operations — providing the visibility, control, and adaptability modern businesses demand.
Open Source vs. Closed Source Software
Software isn’t just categorized by what it does — but also by how it’s built and licensed.
|
Model |
What It Means |
Why Businesses Use It |
|
Open Source |
Source code is openly available and can be modified or extended. |
Flexible, customizable, no vendor lock-in. (e.g., Linux, Apache OFBiz) |
|
Closed Source (Proprietary) |
Source code is owned by a vendor and cannot be altered freely. |
Reliable, fully supported, with regular updates. (e.g., SAP, Microsoft Windows) |
Reality: Most enterprises use a mix of both — proprietary tools for stability and support, open-source platforms for flexibility and customization.
Software, whether open or closed, system-level or application-specific, forms the foundation of digital business today. Understanding these models helps organizations choose tools that align with their goals, workflows, and long-term strategy.
To dive deep you can read the detailed blog on Open Source Software.

What is the Difference Between Software and Hardware?
The distinction between software and hardware lies in their physicality. Hardware refers to the tangible components of a computer or electronic device. In contrast, software is intangible – it comprises the instructions and code that tell the hardware how to operate and perform specific tasks.
What is the Difference Between a Program and Software?
A program is a specific set of instructions written in a programming language to perform a particular task. Software, on the other hand, is a broader term encompassing a collection of programs, procedures, and documentation that work together to enable a computer or electronic device to function.
In simpler terms, a program is a subset of software, and software encompasses all the programs and related components needed for a system to operate effectively.

Is Apache OFBiz™ system software or an application software?
Apache OFBiz can be classified primarily as an application software, and more specifically as an application development framework.
This is because it provides a suite of business applications and tools that cater to specific business needs such as ERP, CRM, ecommerce, and more. Though as an open source ERP it can be used as a central database that connects different areas of business, users still interact with OFBiz as they would typical application software, utilizing its features to perform specific tasks related to their roles within the organization.
It’s also highly favored among developers for the flexible and functional framework it provides.
Conclusion:
The world of software is vast, dynamic, and influences every aspect of our digital lives. From the operating systems that power our devices to the applications that cater to our diverse business, education and entertainment needs, software is the invisible force that drives all our technological tasks.